Constructor/Destructor in C#
By Kamlesh Bhor · 📅 01 Jul 2025 · 👁️ 603
Constructor:
It is used to initialize the variables in the class and used to create object for the class in memory.
Features Of Constructor:
- Constructor name & class name will be same.
- Constructor will be declared as public so that it can be called or executed in main function.
- Constructor will not have return type & will not return value.
- Constructor can contain arguments. It is called parameterized constructor.
- A class can contain more than one constructor. It is called as constructor overloading. A class can contain more than one constructor but there should be difference in a number of arguments or order of arguments or difference in datatypes.
- Default constructor means if the class is not containing constructor then compiler will use default constructor while creating object for the class. Default constructor will never take arguments.
- Private constructor can be accessed within the class. It can be executed with public constructor.
- Static constructor is used to initialize the static variables in a class.
Examples:
1) Constructor containing two arguments:
using System;
namespace Demo
{
class clsEmp
{
public int eno;
public string ename;
public clsEmp(int eno,string ename) //Creating constructor
{
this.eno = eno;
this.ename = ename;
}
public void getdetails()
{
Console.WriteLine(eno + " " + ename);
}
}
class Demo
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
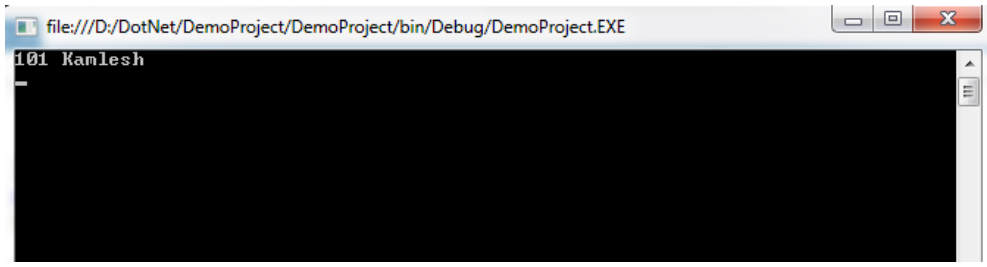
clsEmp obj = new clsEmp(101, "Kamlesh"); //calling constructor
obj.getdetails();
Console.Read();
}
}
}Output:
Note:
'This' represents current class. It is a predefined object in c# used to work with variables in current class.
2) Constructor containing one string argument:
using System;
namespace Demo
{
class clsinfo
{
public string s;
public clsinfo(string s)
{
this.s = s;
}
public void getstring()
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
}
class Demo
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
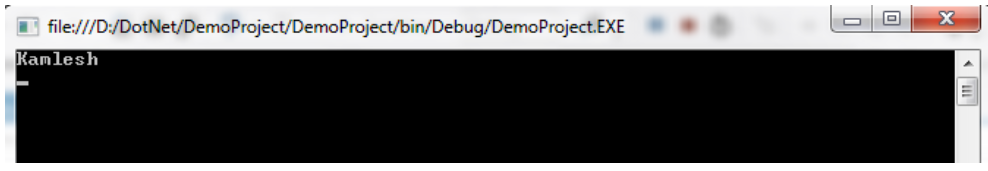
clsinfo obj = new clsinfo("Kamlesh");
obj.getstring();
Console.Read();
}
}
}Output:
3) Constructor containing private & public constructor:
using System;
namespace Demo
{
class clsinfo
{
public string s;
private clsinfo()
{
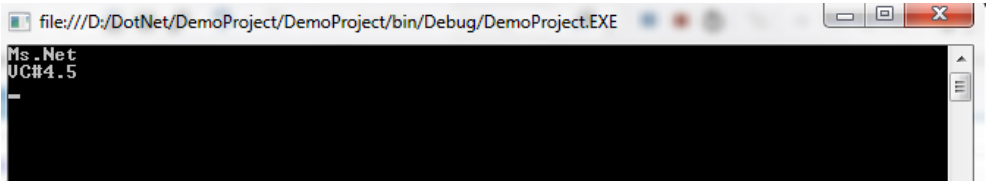
Console.WriteLine("Ms.Net");
}
public clsinfo(string s):this()
{
this.s = s;
}
public void getstring()
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
}
class Demo
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
clsinfo obj=new clsinfo("VC#4.5");
obj.getstring();
Console.Read();
}
}
}Output:
4) Constructor containing two public constructor:
namespace Demo
{
class clsemp
{
public int eno;
public string ename;
public clsemp()
{
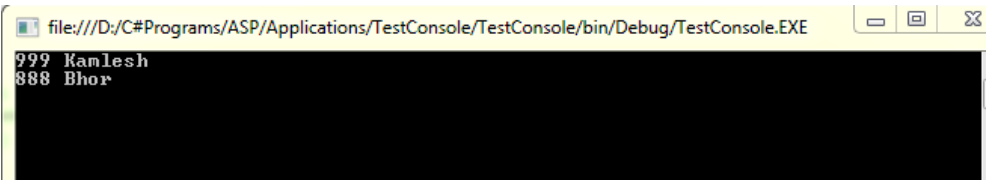
eno=999;
ename="Kamlesh";
Console.WriteLine(eno+" "+ename);
}
public clsemp(int eno,string ename)
{
this.eno = eno;
this.ename = ename;
}
public void getdetails()
{
Console.WriteLine(eno + " " + ename);
}
}
class Demo
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
clsemp obj1 = new clsemp();
clsemp obj2 = new clsemp(888, "Bhor");
obj2.getdetails();
Console.Read();
}
}
}Output:
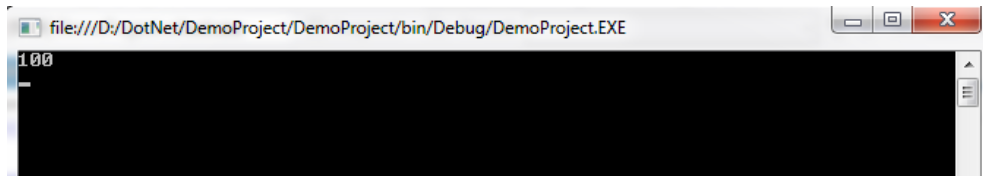
5) Using static constructor:
using System;
namespace Demo
{
class abc
{
public static int a;
static abc()
{
a=100;
}
public static void getA()
{
Console.WriteLine(a);
}
}
class Demo
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
abc.getA();
Console.Read();
}
}
}Output:
Destructor:
Destructor is used to delete object from memory.
Features Of Destructor:
- Destructor name & class name will be same.
- Destructor will start with (~) tilde symbol.
- Destructor will not have return type & will not return value.
- Destructor will not take arguments.
- A class can contain only one destructor.
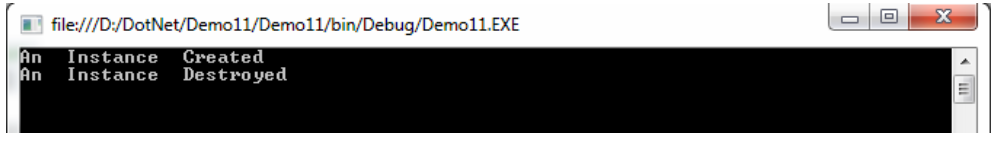
Example of destructor:
using System;
namespace Demo11
{
class Demo
{
// Constructor
public Demo()
{
Console.WriteLine("An Instance Created");
}
// Destructor
~Demo()
{
Console.WriteLine("An Instance Destroyed");
}
}
class Program
{
public static void Test()
{
Demo T = new Demo(); // Created instance of class
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Test();
GC.Collect();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
Note:
Constructor is executed when program execution is started. Destructor will execute before the program execution will end. Constructor will be called in main() & destructor will be called by the compiler. To get the same result window again press ctrl+f5. To delete unreferenced objects from heap memory, System.GC.Collect() should be used.
In this way, we have learned Constructor and destructor with examples in this article. I hope this will help beginners to understand Constructor and destructor.

Article by Kamlesh Bhor
Feel free to comment below about this article.
💬 Join the Discussion